# 填空题
# 1 握手问题
水
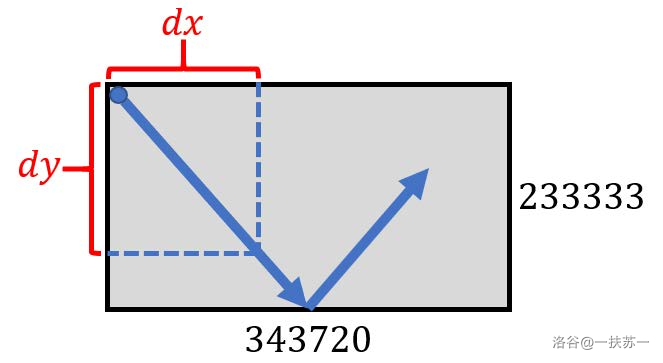
# 2 反弹问题
![]()
对于反弹问题,直接考虑较复杂,而将反弹过程展开,可以得到完整的若干个矩形拼起来。
C++1
2
3
4
5
6
| void solve () {
int a = 343720, b = 233333;
int m = 1059, n = 1768;
printf("%.2lf", sqrt(a * a * m * m + b * b * n * n) * 2);
}
|
# 编程题
# 1 好数
# 题目大意
求 1→n 中有多少个好数
# 题解
C++1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| bool judge(int n) {
bool pd = 1;
while (n != 0) {
if ((n % 10) % 2 != (pd ? 1 : 0))
return false;
pd = !pd, n /= 10;
}
return true;
}
void solve () {
int n, cnt = 0;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (judge(i))
cnt++;
cout << cnt << endl;
}
|
# 2 R 格式
# 题目大意
给定一个整数 n 和一个浮点数 d,你需要
- 将浮点数乘以 2n
- 四舍五入到最接近的整数
# 数据范围
用 t 表示将 d 视为字符串时的长度。
- 对于 50% 的数据,保证 n≤10,t≤15
- 对于全部的测试数据,保证 1≤n≤1000,1≤t≤1024,保证 d 是小数,即包含小数点
# 题解
# 错解(高精乘 + 高精加)
C++1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
| int n;
string d;
string add(string aa, string bb) {
int la = aa.size(), lb = bb.size();
vector<int> a, b, c;
for (int i = la - 1; i >= 0; i--)
a.push_back(aa[i] - '0');
for (int i = lb - 1; i >= 0; i--)
b.push_back(bb[i] - '0');
int t = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < max(la, lb); i++) {
if (i < a.size())
t += a[i];
if (i < b.size())
t += b[i];
c.push_back(t % 10), t /= 10;
}
if (t)
c.push_back(t);
string res = "";
for (int i = c.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
res += to_string(c[i]);
return res;
}
string mul(string aa, string bb) {
int la = aa.size(), lb = bb.size();
vector<int> a, b, c(la + lb, 0);
for (int i = la - 1; i >= 0; i--)
a.push_back(aa[i] - '0');
for (int i = lb - 1; i >= 0; i--)
b.push_back(bb[i] - '0');
for (int i = 0; i < la; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < lb; j++)
c[i + j] = a[i] * b[j];
int lc = c.size() - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < lc; i++)
if (c[i] > 9)
c[i + 1] += c[i] / 10, c[i] %= 10;
while (lc > 0 && c[lc] == 0)
lc--;
string res = "";
for (int i = lc; i >= 0; i--)
res += to_string(c[i]);
return res;
}
void solve () {
cin >> n >> d;
string n2 = "1";
while (n--)
n2 = mul(n2, "2");
int idx = d.find('.');
int xsCnt = d.size() - d.find('.') - 1;
string dd = d.substr(0, idx) + d.substr(idx + 1, xsCnt);
string res = mul(n2, dd);
string zs = res.substr(0, res.size() - xsCnt);
if (res[res.size() - xsCnt] >= '5')
cout << add(zs, "1");
else
cout << zs;
}
|
# 正解
对于 ×2n 的题目,我们可以考虑成不断 ×2,乘 n 次即可,这样就可以把高精度 × 高精度的题目改为高精度 × 低精度了
C++1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| int n;
string d;
string mul(string aa, int b) {
int la = aa.size();
vector<int> a, c;
for (int i = la - 1; i >= 0; i--)
a.push_back(aa[i] - '0');
int t = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < la || t != 0; i++) {
if (i < la)
t += a[i] * b;
c.push_back(t % 10), t /= 10;
}
while (!c.empty() && c.back() == 0)
c.pop_back();
string res = "";
for (int i = c.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
res += to_string(c[i]);
return res;
}
void solve () {
cin >> n >> d;
int idx = d.find('.');
int xsCnt = d.size() - idx - 1;
string dd = d.erase(d.find('.'), 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
dd = mul(dd, 2);
if (dd[dd.size() - xsCnt] < '5')
cout << dd.substr(0, dd.size() - xsCnt);
else {
string res = "";
string ss = dd.substr(0, dd.size() - xsCnt);
reverse(ss.begin(), ss.end());
int t = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < ss.size() || t != 0; i++) {
if (i < ss.size())
t += ss[i] - '0';
res += to_string(t % 10), t /= 10;
}
for (int i = res.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--)
cout << res[i];
}
}
|
# 3 宝石组合
# 题目大意
对于 n 个数 a1,...,an,找出 MAX(gcd(a[i], a[j], a[k]) 的最小字典序
# 数据范围
- 1≤n≤105
- 1≤ai≤105
# 题解